Understanding and Managing Thrombosis and Embolism of Blood Vessels
What Are Thrombosis and Embolism?
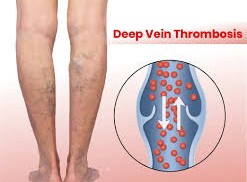
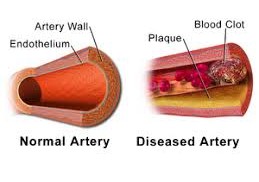
Have you ever wondered why blood sometimes forms dangerous clots that can block blood vessels? Thrombosis and embolism are serious conditions that occur when blood flow is obstructed by a clot.
- Thrombosis happens when a blood clot forms inside a vein or artery.
- Embolism occurs when a piece of the clot breaks off and travels through the bloodstream, blocking another vessel.
- These conditions can cause heart attacks, strokes, or lung blockages if not managed properly.
Both problems disturb the normal flow of blood, leading to tissue damage and sometimes life-threatening situations. It is important to detect and treat these conditions early to prevent complications. When the balance between clot formation and clot breakdown is disrupted, it can lead to harmful blockages. Understanding their causes and prevention can save lives.
Why Do Blood Clots Form?
Blood clots are the body’s natural way to stop bleeding, but sometimes they form when they are not needed.
- Lack of movement for long periods (such as sitting or bed rest).
- Injury to a blood vessel’s wall.
- Chronic diseases like diabetes or heart failure.
- Genetic factors that increase clotting tendency.
When these factors combine, the risk of thrombosis or embolism increases. Staying active, avoiding smoking, and maintaining a healthy diet can help keep the blood flowing normally. This shows that both lifestyle and health conditions contribute to the risk of developing blood clots, making prevention a daily responsibility.
Symptoms to Watch For
How can you tell if you might have a clot? Recognizing symptoms early can prevent serious outcomes.
- Pain or swelling in one leg or arm.
- Redness or warmth in the affected area.
- Shortness of breath or chest pain (possible signs of a lung clot).
- Sudden numbness or confusion, which can signal a stroke.
These symptoms should never be ignored, especially if they appear suddenly. Getting medical attention quickly helps doctors act before the clot causes damage. This highlights that awareness of the body’s signals is vital to preventing severe complications.
Preventive Lifestyle Measures
How can we lower the risk of thrombosis and embolism naturally? Prevention begins with everyday habits.
- Stay active by walking or stretching regularly.
- Eat balanced meals rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats.
- Avoid dehydration by drinking enough water.
- Quit smoking, as it damages blood vessels.
- Maintain healthy weight to reduce pressure on veins.
These actions strengthen blood vessels and improve circulation. Simple daily changes can significantly reduce the risk of clots. Healthy habits remain one of the strongest shields against these vascular conditions.
Medical Treatments for Thrombosis and Embolism
What happens when lifestyle measures are not enough? Medical treatments are available to manage and prevent clots.
- Blood thinners help prevent new clots from forming.
- Compression stockings support vein health and blood flow.
- Surgical procedures may be needed to remove large clots.
Doctors carefully monitor patients to find the safest and most effective treatment. Medications that reduce clotting power must be used under professional guidance. This demonstrates that while prevention is key, medical treatment plays a crucial role in controlling the condition.
The Role of Coumadin (Warfarin) in Treatment
Can medications like Coumadin make a difference in treating thrombosis? Yes, they play a key role in preventing new blood clots.
- Coumadin (Warfarin) helps slow down the clotting process in the blood.
- It allows blood to move more freely through veins and arteries.
- Regular blood tests are needed to ensure it works safely and effectively.
- Doctors adjust the dose to fit each person’s unique condition.
This medication, when monitored properly, is one of the most trusted tools for reducing clot-related risks. Proper use of Coumadin can transform long-term outcomes for patients with a history of thrombosis or embolism.
Coumadin in Preventing Recurrence
How does Coumadin help in preventing future blood vessel problems? Its long-term benefits are widely recognized.
- Prevents new clots from forming in people with past episodes.
- Reduces stroke risk in those with irregular heartbeat.
- Protects the lungs and heart from clot-related damage.
- Supports stable circulation with consistent medical follow-up.
With careful supervision, Coumadin helps maintain a healthy balance between clot prevention and safe blood flow.
This makes Coumadin a cornerstone of ongoing protection against thrombosis and embolism.
Living Safely with Thrombosis and Embolism
How can people live well after diagnosis? A balanced approach of lifestyle, regular check-ups, and proper medication can ensure a safe life. Follow doctor’s advice and attend regular monitoring visits. Take prescribed medicines exactly as directed. Avoid risky behaviors, such as smoking or sitting for long hours. Stay informed about early symptoms and act quickly. Living with these conditions is manageable with discipline and awareness. The key lies in partnership between patient and healthcare provider. Managing thrombosis and embolism requires understanding, prevention, and consistent care guided by medical professionals.
Drug Description Sources:U.S. National Library of Medicine, Drugs.com, WebMD, Mayo Clinic, RxList, MedlinePlus, Cleveland Clinic, Healthline, Johns Hopkins Medicine, National Heart Lung and Blood Institute.
Reviewed and Referenced By:
- Dr. Alan Carter, PharmD – Clinical pharmacist specializing in blood-thinning therapies and vascular conditions, frequently cited on Drugs.com and RxList.
- Dr. Maria Bennett, MD – Cardiologist affiliated with Mayo Clinic, contributor to WebMD and the National Library of Medicine resources on circulatory health.
- Dr. Thomas Rivera, MD, PhD – Hematologist and researcher at Johns Hopkins Medicine, referenced for insights on safe anticoagulant use.
- Dr. Elaine Turner, RN, MSN – Clinical nurse educator contributing to patient safety information across MedlinePlus and Healthline.
Article Post: Editorial Team of RXShop.md
(Updated at Oct 31 / 2025)