Women’s brains are more active than men’s, study shows
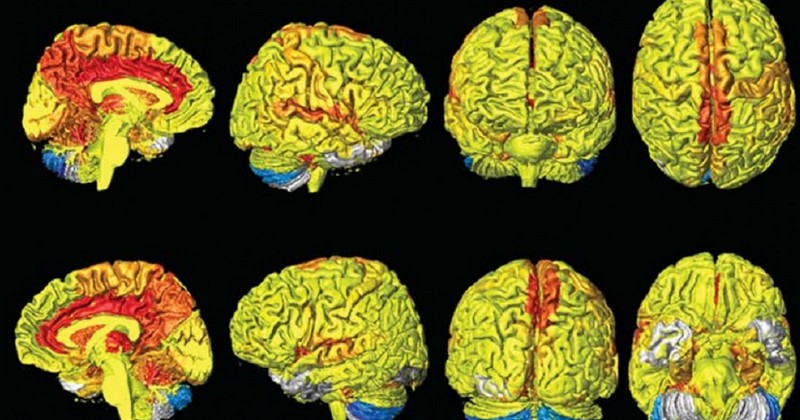
The differences between the sexes are also reflected in the degree of brain activation.
The psychological and neurological differences between men and women are one of the most are one of the most interesting fields of study in the world of science applied to the study of human beings. Ultimately, the division between the sexes has a clear impact on many aspects of our lives, no matter what culture we belong to, all over the world.
For example, research that explores differences in cognitive performance between men and women is intended to give us an approximation of the type of mental abilities and psychological aptitudes. Typically, this is done by differentiating between categories of cognitive abilities and seeing which ones women excel at and which ones men tend to be better at.
However, there are other indirect ways of knowing which aspects of our mental life are divided between the sexes. For example, it is possible to see to what extent people's brains tend to be activated.. And that is exactly what has been done by a recent study, the results of which have been published in the scientific journal Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. The conclusion is that, in general, women's brains are more or less 10% more active than men's brains.
Women's brains are more active
This research driven by scientists at Amen Clinics in California was conducted on the basis of more than 20,000 images in which the functional activation of the brains of women and men is recorded. recording the functional activation of patients' brains..
These "scans" of the brain are performed by measuring which areas of this set of organs receive the greatest amount of Blood flow. The idea is based on the idea that the more blood reaches an area, the more "activated" it will be, since the irrigation comes to support the energy needs of the areas that need a greater amount of resources because they are very busy.
Thus, based on the coloration and brightness received by each of the areas of the brain, the researchers were able to see how in the brains of women it was more frequent to have "illuminated" brain extensions of larger brain extensions than in men (at least in proportion).
From the data analysis, it was seen that women's brains were larger both at rest (a 12% difference) and while performing a complex task (in this case, the difference was 8%).
Are women smarter?
It is very easy and intuitive to relate the activation of the brains with the degree of intelligence. However, they are two different things.
What defines intelligence itself is the ability to improvise solutions in changing situations. In other words, if we are we are good at adapting to rapidly changing contexts, we will be intelligent regardless of what we do.In other words, if we are good at adapting to rapidly changing contexts, we will be intelligent regardless of what happens in our brains: what matters is the practice of our actions applied to real environments, not neuroimaging.
However, it is also true that our actions are not disconnected from what happens in our brain, far from it (without a brain, there would be no behavior). And furthermore, virtually any variation in behavioral patterns is embodied in differences in activation patterns. That is why the fact that women's brains tend to be somewhat more activated than men's is much more than just a curiosity, and may have implications in the world of psychology and neuroscience..
For example, there is data showing how intelligence is linked more to low brain activation than to high brain activation. It makes sense, since the most intelligent people make less effort when it comes to executing complex mental operations. They manage their neural resources better, so to speak.
But this does not mean that women are less intelligent than men. In the end, the records of IQ scores reveal that there are hardly any differences between the two sexes, and that in any case the average intelligence of women is somewhat higher than that of men, while the number of gifted people is higher in men, and the same is true for extremely low scores (in this sex there is a greater dispersion of results).
Are they really differences between sexes?
The existence of these differences in the intensity of brain activation does not mean that in any situation and context, the female brain always maintains this difference with respect to the male brain. As much as there are several differences between men and women that are almost entirely due to genes, others are the result of cultureThe way society shapes our nervous systems.
What happens is that, so far, it is not clear which part of the observable differences between men and women are due to genetics and which are due to culture. More research will be needed to find out whether it is all due to the different lifestyles of the sexes. is due to the different lifestyles of the sexes.. We often forget that, even across cultures, the roles assigned to women and men can cause their nervous systems to adapt in different ways.
(Updated at Apr 14 / 2024)