Be afraid of needles
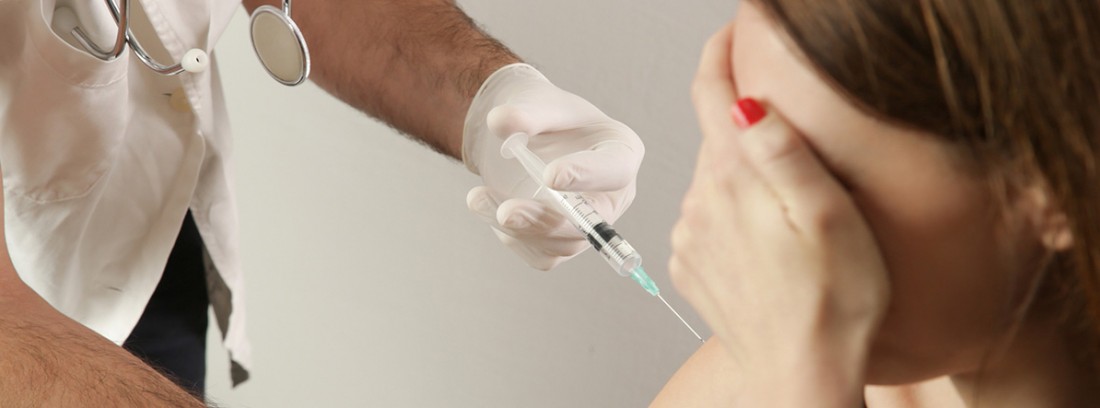
Belonephobia is a subtype of a more global phobia which is called aicnophobia or trypanophobia, which refers to the fear of pointed or sharp objects of all kinds, which can pierce or drill. Specifically, belenephobia is characterized by a intense, irrational, and persistent fear of needles and that generates avoidance behaviors in the event of receiving an injection.
It is often confused with hematophobia or fear of blood (Although blood can be produced in other ways, not just a prick), and in fact the treatment is very similar.
It is one of the most common phobias, around a 12% of the population suffers from it. It is common in children, but also in adults. The causes for developing this phobia are diverse:
- By classical conditioning or associative learning. If you've had a bad needle experience once, you may tend to fear that it will happen again.
- By vicarious conditioning or observational learning. If you see the suffering of someone related to needles, you may tend to incorporate that fear in the first person.
- By hereditary component. The physiological overcompensation mechanism can be passed from one generation to another.
How does the body react?
The symptomatology that characterizes belonephobia manifests itself in three different planes:
- Physical: cold sweats, tremors, feeling short of breath, dizziness, sweating, rapid heartbeat, fainting ...
- Cognitive: interpretation of somatic symptoms as dangerous, irrational thoughts, confusion, lack of concentration ...
- Behavioral: avoidance and escape behaviors.
It is important to bear in mind that this type of phobia is very marked by the anticipatory anxiety, which is what blocks the dreaded behavior from taking place (the injection itself). Just thinking about an injection can generate symptoms in the most serious cases.
Symptoms of fear of needles
It is one of the least studied phobias, despite the fact that it has certain characteristics that make it particular.
Usually, phobias program us to flee from the dreaded situation, increasing the heart rate, blood pressure and respiratory rate and creating vasoconstriction of the peripheral vessels, which physiologically prepares us to run.
Belonephobia produces:
- Decrease in circulation sanguine
- Decrease in heart rate
- Dilation of the blood vessels, which in the most severe cases leads to Fainting (vasovagal syncope) because not enough blood is reaching the brain.
Consequences of being afraid of needles
What makes it a potentially harmful phobia is that it can make you preventive actions are avoided for health such as:
- Disease screening tests
In parallel, it can also affect conception. Many women who avoid pregnancy are fearful of various medical tests involving needles.
You can also do that avoid the dentist and in the most serious cases, where the phobia is increasing, there may be a fear of entering any medical center, even as a companion to a patient.
How to treat this phobia?
- Learn to manage anticipatory anxiety It begins only by imagining the needle. Readjust the chains of thoughts: what scares you is not the needle itself (it is an object), but the thoughts that you have associated with it (for example, “I'm going to pass out”). In the same way that you have associated a type of anxious thoughts, you can also retrain and learn to associate them with neutral stimuli.
- Know the physiological mechanisms why fainting occurs and what increases its likelihood (for example, hunger, heat, sudden change in position, standing for a long time, etc.).
- Train your fear in imagination: Imagine feared situations while practicing until your anxiety is reduced. You see it increasing in intensity, it begins with less powerful fears (like being in the waiting room) and increases until the most feared moment (like when you feel the cold of the needle on your skin).
- Enrich Imagination Techniques with Other Sensory Stimuli. It is about evoking in the most realistic way possible the sensations of the dreaded situation, for example, the smell of alcohol, pressure of a rubber band around the arm, noticing the cold with other metallic objects that are not a needle ...
- Expose yourself to fear progressively: once you have worked on fear in your imagination and it is no longer threatening, start practicing “live” situations. For example, being in a real waiting room, accompanying someone to donate blood, etc.
- If the fear is uncontrollable, consult a psychotherapist. They have a wide medical team of psychology specialists who can help you treat this type of phobia.
CALCULATE YOUR PRICE
- Belonephobia is part of a more global type of phobia called aichnophobia or trypanophobia, which refers to the fear of pointed or sharp objects of all kinds, which can puncture or pierce.
- It is one of the least studied phobias, despite the fact that it has certain characteristics that make it particular.
- There are techniques that can help to overcome it, but if this phobia proves uncontrollable it is advisable to consult a psychotherapist.
(Updated at Apr 13 / 2024)