Understanding and Managing Tuberculosis: A Complete Guide
What Is Tuberculosis and Why Does It Matter?
Tuberculosis is a serious infection that mainly affects the lungs, but it can also spread to other parts of the body like the brain, kidneys, or spine. It is caused by bacteria that spread from person to person through the air when someone with the disease coughs, sneezes, or even speaks. Tuberculosis can remain hidden in the body for years without causing symptoms. When active, it can lead to coughing, fever, weight loss, and tiredness. If not treated properly, it can cause long-term damage and even be life-threatening. It spreads more easily in crowded places or where people live close together. Early detection and full treatment are important to prevent spreading the infection. Many people do not realize they have it until symptoms become strong. This is why awareness and regular check-ups in high-risk areas are very important.
How Does Tuberculosis Spread?
Tuberculosis spreads through the air when an infected person releases tiny droplets by coughing, sneezing, or talking. It is not spread by touching surfaces or sharing food, but being close to someone who is sick increases the risk.
- People with active lung tuberculosis are the most likely to spread it.
- You can get infected by being in close contact with an untreated person.
- It does not spread through handshakes or touching objects.
- Poor ventilation, weak immune systems, and crowded living conditions make spread easier.
Understanding how it spreads helps protect yourself and others by promoting good hygiene, wearing masks in high-risk areas, and ensuring sick individuals get medical care quickly.
Symptoms That Should Not Be Ignored
Tuberculosis symptoms may start mildly and grow worse over time. Many people think they just have a cold or are tired, but certain signs point to something more serious.
- A cough that lasts more than 3 weeks
- Coughing up mucus or even blood
- Chest pain, especially while breathing or coughing
- Night sweats, fever, or chills
- Feeling tired all the time and sudden weight loss
If someone experiences these symptoms, especially with a known exposure to the disease, they should see a doctor right away. Early diagnosis makes treatment easier and recovery faster.
Who Is Most at Risk of Tuberculosis?
Some people are more likely to get tuberculosis than others, especially if their bodies have a harder time fighting infections.
- People with weakened immune systems (for example, due to long-term illness or poor nutrition)
- Individuals living or working in crowded places such as shelters or prisons
- People who have not received proper medical care in the past
- Children and elderly people
- Health workers who are around infected patients often
Knowing who is at higher risk allows for better protection and earlier testing. Simple measures like wearing masks and regular screening can reduce the chances of catching tuberculosis.
Diagnosing and Monitoring the Illness
Getting tested for tuberculosis usually includes a skin test or a chest X-ray. Doctors also check sputum samples, which are fluids from the lungs, to find the bacteria.
- Chest X-rays help find signs of lung damage or infection.
- Doctors may ask for three sputum samples to confirm the diagnosis.
- Blood tests may be done to check the immune system’s response.
- Treatment should begin right after confirmation of the illness.
Testing is quick and not painful. People who live in areas where tuberculosis is common should be tested regularly to catch the infection early.
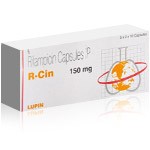
Treating Tuberculosis with R-Cin (Rifampicin)
Tuberculosis can be treated successfully with the right medicines taken over several months. One of the main medications used is R-Cin, which contains Rifampicin. This medicine works by killing the bacteria causing the infection and stopping them from growing.
- R-Cin is usually taken daily as part of a treatment plan with other medicines.
- It is important to take the full course of treatment without missing doses.
- Stopping the treatment too early can cause the infection to return and become harder to treat.
- Doctors may recommend regular check-ups to watch for side effects and to see how well the medicine is working.
In most cases, people begin to feel better after a few weeks, but the full treatment can last from 6 to 9 months. Even if the symptoms go away, it is very important to continue taking all prescribed medicine.
R-Cin has helped many people fully recover from tuberculosis. It is a powerful tool in fighting this disease when used correctly and under a doctor’s guidance. Along with a healthy diet and rest, this treatment gives patients a strong chance of complete recovery. Patients should also avoid alcohol and other medicines unless approved by their doctor during treatment, as R-Cin can affect how the body processes other substances. Tuberculosis can be a scary illness, but with awareness, testing, and proper treatment, it can be managed and cured. Early attention to symptoms, understanding how it spreads, and following the full course of medication can help individuals fully recover and prevent the spread to others.
Article Post: Editorial Team of RXShop.md
(Updated at Jul 19 / 2025)